We're for all- ALL are for us for the greater interest of Humanism-Truth-Facts-Friendship-Unity-Participation including Physico-Mental Sound Health with Spirituality enrichment through ''TOTAL HEALTH SOLUTION'' to a Well-furnished GOALofTruth alloted for all in real sense ;
From wikipedia & other reliable sources ( Poets, Writers, Thinkers, Researchers, Free Lancers, Philosophers, Theologists, Scientists, Orators, Sociologists and Photographers +Artists-Musicians & etc.) we can learn as follows :
''A distinguishing characteristic of the class Mammalia is the presence of mammary glands. Mammary glands are modified sweat glands that produce milk, which is used to feed the young for some time after birth. Only mammals produce milk. Mammary glands are obvious in humans, because the female human body stores large amounts of fatty tissue near the nipples, resulting in prominent breasts. Mammary glands are present in all mammals, although they are normally redundant in males of the species.[25]
Most mammalian females have two copies of the X chromosome, while males have only one X and one smaller Y chromosome; some mammals, such as the platypus, have different combinations.[26][27] One of the female's X chromosomes is randomly inactivated in each cell of placental mammals while the paternally derived X is inactivated in marsupials. In birds and some reptiles, by contrast, it is the female which is heterozygous and carries a Z and a W chromosome while the male carries two Z chromosomes. In mammals, females can have XXX or X.[28][29]
Mammalian females bear live young, with the exception of monotreme females, which lay eggs.[30] Some non-mammalian species, such as guppies, have analogous reproductive structures; and some other non-mammals, such as some sharks, also bear live young.[31]
In sex determination for mammals, female is the default sex, while in the poplar genus Populus the default is male''.[32]
Maternal complications[edit]
''A puerperal disorder or postpartum disorder is a complication which presents primarily during the puerperium, or postpartum period. The postpartum period can be divided into three distinct stages; the initial or acute phase, six to 12 hours after childbirth; subacute postpartum period, which lasts two to six weeks, and the delayed postpartum period, which can last up to six months. In the subacute postpartum period, 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem.[115][116] Long-term health problems (persisting after the delayed postpartum period) are reported by 31 per cent of women.[117]
Postpartum bleeding[edit]
According to the WHO, hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal death worldwide accounting for approximately 27.1% of maternal deaths.[118] Within maternal deaths due to hemorrhage, two-thirds are caused by postpartum hemorrhage.[118] The causes of postpartum hemorrhage can be separated into four main categories: Tone, Trauma, Tissue, and Thrombin. Tone represents uterine atony, the failure of the uterus to contract adequately following delivery. Trauma includes lacerations or uterine rupture. Tissue includes conditions that can lead to a retained placenta. Thrombin, which is a molecule used in the human body’s blood clotting system, represents all coagulopathies.[119]
Postpartum infections[edit]
Postpartum infections, also historically known as childbed fever and medically as puerperal fever, are any bacterial infections of the reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage. Signs and symptoms usually include a fever greater than 38.0 °C (100.4 °F), chills, lower abdominal pain, and possibly bad-smelling vaginal discharge. The infection usually occurs after the first 24 hours and within the first ten days following delivery. Infection remains a major cause of maternal deaths and morbidity in the developing world. The work of Ignaz Semmelweis was seminal in the pathophysiology and treatment of childbed fever and his work saved many lives.[120]
Childbirth can be an intense event and strong emotions, both positive and negative, can be brought to the surface. Abnormal and persistent fear of childbirth is known as tokophobia. The prevalence of fear of childbirth around the world ranges between 4–25%, with 3–7% of pregnant women having clinical fear of childbirth.[121][122]
Most new mothers may experience mild feelings of unhappiness and worry after giving birth. Babies require a lot of care, so it is normal for mothers to be worried about, or tired from, providing that care. The feelings, often termed the "baby blues", affect up to 80 per cent of mothers. They are somewhat mild, last a week or two, and usually go away on their own.[123]
Postpartum depression is different from the "baby blues". With postpartum depression, feelings of sadness and anxiety can be extreme and might interfere with a woman's ability to care for herself or her family. Because of the severity of the symptoms, postpartum depression usually requires treatment. The condition, which occurs in nearly 15 percent of births, may begin shortly before or any time after childbirth, but commonly begins between a week and a month after delivery.[123]
Childbirth-related posttraumatic stress disorder is a psychological disorder that can develop in women who have recently given birth.[124][125][126] Causes include issues such as an emergency C-section, preterm labour, inadequate care during labour, lack of social support following childbirth, and others. Examples of symptoms include intrusive symptoms, flashbacks and nightmares, as well as symptoms of avoidance (including amnesia for the whole or parts of the event), problems in developing a mother-child attachment, and others similar to those commonly experienced in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Many women who are experiencing symptoms of PTSD after childbirth are misdiagnosed with postpartum depression or adjustment disorders. These diagnoses can lead to inadequate treatment.[127]
Postpartum psychosis is a rare psychiatric emergency in which symptoms of high mood and racing thoughts (mania), depression, severe confusion, loss of inhibition, paranoia, hallucinations and delusions set in, beginning suddenly in the first two weeks after childbirth. The symptoms vary and can change quickly.[128] It usually requires hospitalisation. The most severe symptoms last from two to 12 weeks, and recovery takes six months to a year.[128]
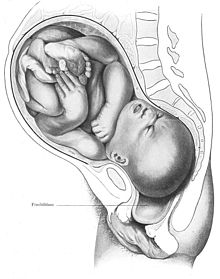
Fetal complications[edit] Mechanical fetal injury may be caused by improper rotation of the fetus. Five causes make up about 80 per cent of newborn deaths globally: prematurity, low-birth-weight, infections, lack of oxygen at birth, and trauma during birth.[20]
Mechanical fetal injury may be caused by improper rotation of the fetus. Five causes make up about 80 per cent of newborn deaths globally: prematurity, low-birth-weight, infections, lack of oxygen at birth, and trauma during birth.[20]
Stillbirth[edit]
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.[129][130] It results in a baby born without signs of life.[130]
Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health systems.[130][131] About half of stillbirths occur during childbirth, and stillbirth is more common in the developing than developed world.[130] Otherwise depending on how far along the pregnancy is, medications may be used to start labour or a type of surgery known as dilation and evacuation may be carried out.[132] Following a stillbirth, women are at higher risk of another one; however, most subsequent pregnancies do not have similar problems.[133]
Worldwide in 2019 there were about 2 million stillbirths that occurred after 28 weeks of pregnancy, this equates to 1 in 72 total births or one every 16 seconds.[134] Still births are more common in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa.[130] Stillbirth rates have declined, though more slowly since the 2000s.[135]
Preterm birth[edit]
Preterm birth is the birth of an infant at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age. Globally, about 15 million infants were born before 37 weeks of gestation.[136] Premature birth is the leading cause of death in children under five years of age though many that survive experience disabilities including learning defects and visual and hearing problems. Causes for early birth may be unknown or may be related to certain chronic conditions such as diabetes, infections, and other known causes. The World Health Organization has developed guidelines with recommendations to improve the chances of survival and health outcomes for preterm infants.[137][138]
If a pregnant woman enters preterm labour, delivery can be delayed by giving medications called tocolytics. Tocolytics delay labour by inhibiting contractions of the uterine muscles that progress labor. The most widely used tocolytics include beta agonists, calcium channel blockers, and magnesium sulfate. The goal of administering tocolytics is not to delay delivery to the point that the child can be delivered at term, but instead to postponing delivery long enough for the administration of glucocorticoids which can help the fetal lungs to mature enough to reduce morbidity and mortality from infant respiratory distress syndrome.[138]
Post-term birth[edit]
The term postterm pregnancy is used to discribe a condition in which a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the usual 40-week duration of pregnancy.[139] Postmature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including meconium aspiration syndrome, fetal malnutrition, and stillbirths.[140] The placenta, which supplies the baby with oxygen and nutrients, begins to age and will eventually fail after the 42nd week of gestation. Induced labor is indicated for postterm pregnancy.[141][142][143]
Neonatal infection[edit]
Newborns are prone to infection in the first month of life. The pathogenic bacterium Streptococcus agalactiae (a group B streptococcus) is most often the cause of these occasionally fatal infections. The baby contracts the infection from the mother during labour. In 2014 it was estimated that about one in 2000 newborn babies had a group B streptococcuss infection within the first week of life, usually evident as respiratory disease, general sepsis, or meningitis.[145]
Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are associated with birth defects, and infections in newborn babies, particularly in the areas where rates of infection remain high. The majority of STIs have no symptoms or only mild symptoms that may not be recognised. Mortality rates resulting from some infections may be high, for example the overall perinatal mortality rate associated with untreated syphilis is 30 per cent.[146]
Perinatal asphyxia[edit]
Perinatal asphyxia is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm.[147] Hypoxic damage can also occur to most of the infant's organs (heart, lungs, liver, gut, kidneys), but brain damage is of most concern and perhaps the least likely to quickly or completely heal.[147] Oxygen deprivation can lead to permanent disabilities in the child, such as cerebral palsy.[148]
Mechanical fetal injury[edit]
Risk factors for fetal birth injury include fetal macrosomia (big baby), maternal obesity, the need for instrumental delivery, and an inexperienced attendant. Specific situations that can contribute to birth injury include breech presentation and shoulder dystocia. Most fetal birth injuries resolve without long term harm, but brachial plexus injury may lead to Erb's palsy or Klumpke's paralysis''.[149]
We're for all- ALL are for us for the greater interest of Humanism-Truth-Facts-Friendship-Unity-Participation to a Well-furnished GOAL of Truth from which all shall have ++++;
We're indebted to WIKIPEDIA +WHO for a short while and as 'Guardian QUOTATION' from Global WISER ONE. And have quoted many images, article's, writings etc. by great & humanist writers+++ from global thinkers, Well-wishers, Wiseman, Humanists and Others Living-Nonlivings in favor of HUMANISM to share more answers of Researchers-readers+++++....
To reach the 'GOAL of FULFILNESS' unitedly to alive in the "DESTINATION of TRUTH-FACTS-CHARMEST AMICABLITY" of Natural Joyful POSSIBILITIES+++
BREAST CANCER, TUMOR, Arsenic+Chemical Poisoning, Corona, Heart-Lung diseases, Neurological-Hormonal-Immunal-Infectious diseases with related complexities are possible to cure properly-easily-scientifically-accurately (100%) by our positive medical services only with+++++balance confirming
Medicine-Food control-proper nursing-medicinal massage-Medicinal Yogas- Meditation, Physiotherapy special etc. without side effects & Repeatation as per contract through user-friendly approved ways of CURE++++. please fill our form as below or click:
After confirming contract-letter between you+++. We serve you properly with no Chemo-therapy-radiation therapy -SURGICAL Complexities (Physical-Mental) to CURE+++ upto our Limit to recover your both-health from illness.