- Hits: 1358
- Video Field: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iKPw6-cTpIA
We're for all- ALL are for us for the greater interest of Humanism-Truth-Facts-Friendship-Unity-Participation including Physico-Mental Sound Health with Spirituality enrichment through ''TOTAL HEALTH SOLUTION'' to a Well-furnished GOALofTruth alloted for all in real sense ;
From wikipedia & other reliable sources ( Poets, Writers, Thinkers, Researchers, Free Lancers, Philosophers, Theologists, Scientists, Orators, Sociologists and Photographers +Artists-Musicians & etc.) we can learn as follows :
-

Physical fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of sports, occupations and daily activities. Physical fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition,[1] moderate-vigorous physical exercise,[2] and sufficient rest along with a formal recovery plan.[3]
Before the Industrial Revolution, fitness was defined as the capacity to carry out the day's activities without undue fatigue or lethargy. However, with automation and changes in lifestyles, physical fitness is now considered a measure of the body's ability to function efficiently and effectively in work and leisure activities, to be healthy, to resist hypokinetic diseases, improve immune system and to meet emergency situations
Mental fitness[edit]
Mental fitness is a mental health movement that encourages people to intentionally regulate and maintain their emotional wellbeing through friendship, regular human contact, and activities that include meditation, calming exercises, aerobic exercise, mindfulness, having a routine and maintaining adequate sleep. Mental fitness is intended to build resilience against every-day mental health challenges to prevent an escalation of anxiety, depression and suicidal ideation, and help them cope with the escalation of those feelings if they occur.[125]
Spiritual counseling[edit]
Spiritual counsellors meet with people in need to offer comfort and support and to help them gain a better understanding of their issues and develop a problem-solving relation with spirituality. These types of counselors deliver care based on spiritual, psychological and theological principles.[126]
Laws and public health policies[edit]
There are many factors that influence mental health including:
- Mental illness, disability, and suicide are ultimately the result of a combination of biology, environment, and access to and utilization of mental health treatment.
- Public health policies can influence access and utilization, which subsequently may improve mental health and help to progress the negative consequences of depression and its associated disability.
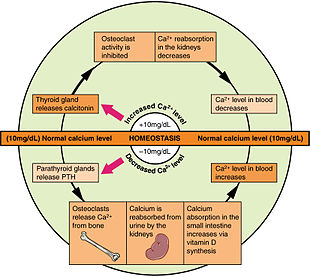
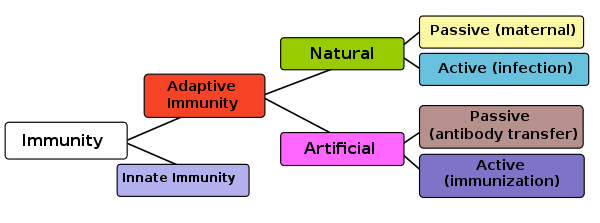
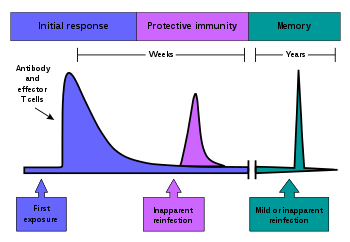
n biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens irrespective of their antigenic make-up. Other components of the immune system adapt themselves to each new disease encountered and can generate pathogen-specific immunity.
Immunity is a complex biological system that can recognize and tolerate whatever belongs to the self, and to recognize and reject what is foreign (non-self)
The meaning of spirituality [1] has developed and expanded over time, and various meanings can be found alongside each other.[2][3][4][note 1] Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape of man",[note 2] oriented at "the image of God"[5][6] as exemplified by the founders and sacred texts of the religions of the world. The term was used within early Christianity to refer to a life oriented toward the Holy Spirit[7] and broadened during the Late Middle Ages to include mental aspects of life.[8]
In modern times, the term both spread to other religious traditions[9] and broadened to refer to a wider range of experiences, including a range of esoteric and religious traditions. Modern usages tend to refer to a subjective experience of a sacred dimension[10] and the "deepest values and meanings by which people live",[11][12] often in a context separate from organized religious institutions.[7] This may involve belief in a supernatural realm beyond the ordinarily observable world,[13] personal growth,[14] a quest for an ultimate or sacred meaning,[15] religious experience,[16] or an encounter with one's own "inner dimension"
- Hits: 1344
- Video Field: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iKPw6-cTpIA
We're for all- ALL are for us for the greater interest of Humanism-Truth-Facts-Friendship-Unity-Participation including Physico-Mental Sound Health with Spirituality enrichment through ''TOTAL HEALTH SOLUTION'' to a Well-furnished GOALofTruth alloted for all in real sense ;
From wikipedia & other reliable sources ( Poets, Writers, Thinkers, Researchers, Free Lancers, Philosophers, Theologists, Scientists, Orators, Sociologists and Photographers +Artists-Musicians & etc.) we can learn as follows :

![]()
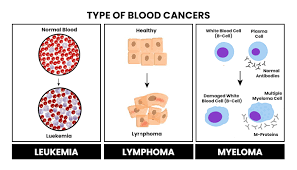
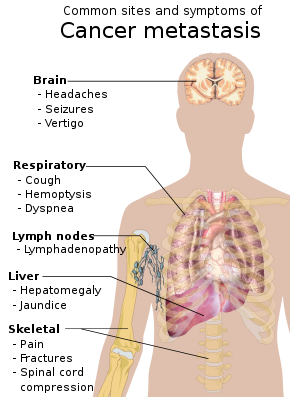
''Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body.[2][7] These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread.[7] Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements.[1] While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes.[1] Over 100 types of cancers affect humans.[7]
Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths.[2] Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol.[2][8][9] Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants.[3] In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as Helicobacter pylori, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).[2] These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of a cell.[10] Typically, many genetic changes are required before cancer develops.[10] Approximately 5–10% of cancers are due to inherited genetic defects.[11] Cancer can be detected by certain signs and symptoms or screening tests.[2] It is then typically further investigated by medical imaging and confirmed by biopsy.[12]
The risk of developing certain cancers can be reduced by not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, eating plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, eating resistant starch,[13] vaccination against certain infectious diseases, limiting consumption of processed meat and red meat, and limiting exposure to direct sunlight.[14][15] Early detection through screening is useful for cervical and colorectal cancer.[16] The benefits of screening for breast cancer are controversial.[16][17] Cancer is often treated with some combination of radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy and targeted therapy.[2][4] Pain and symptom management are an important part of care.[2] Palliative care is particularly important in people with advanced disease.[2] The chance of survival depends on the type of cancer and extent of disease at the start of treatment.[10] In children under 15 at diagnosis, the five-year survival rate in the developed world is on average 80%.[18] For cancer in the United States, the average five-year survival rate is 66%.[5]
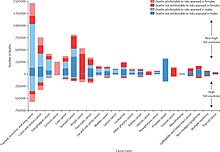
In 2015, about 90.5 million people worldwide had cancer.[19] In 2019, annual cancer cases grew by 23.6 million people and there were 10 million deaths worldwide, representing over the previous decade increases of 26% and 21%, respectively.[6][20]
The most common types of cancer in males are lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, and stomach cancer.[21] In females, the most common types are breast cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, and cervical cancer.[10] If skin cancer other than melanoma were included in total new cancer cases each year, it would account for around 40% of cases.[22][23] In children, acute lymphoblastic leukemia and brain tumors are most common, except in Africa, where non-Hodgkin lymphoma occurs more often.[18] In 2012, about 165,000 children under 15 years of age were diagnosed with cancer.[21] The risk of cancer increases significantly with age, and many cancers occur more commonly in developed countries.[10] Rates are increasing as more people live to an old age and as lifestyle changes occur in the developing world.[24] The global total economic costs of cancer were estimated at US$1.16 trillion per year as of 2010.[25]
- Hits: 1305
- Video Field: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iKPw6-cTpIA
We're for all- ALL are for us for the greater interest of Humanism-Truth-Facts-Friendship-Unity-Participation including Physico-Mental Sound Health with Spirituality enrichment through ''TOTAL HEALTH SOLUTION'' to a Well-furnished GOALofTruth alloted for all in real sense ;
From wikipedia & other reliable sources ( Poets, Writers, Thinkers, Researchers, Free Lancers, Philosophers, Theologists, Scientists, Orators, Sociologists and Photographers +Artists-Musicians & etc.) we can learn as follows :
Plz fill the under quoted "Primary Patient Form" for most urgent Ideal Curative Medical Care & Services to Gain your Former Sound Health by the 500%proved +Accurate Innovative Healing TOOLS.... without Conditional "DEATH-RISKS


Malaria has several serious complications, including the development of respiratory distress, which occurs in up to 25% of adults and 40% of children with severe P. falciparum malaria. Possible causes include respiratory compensation of metabolic acidosis, noncardiogenic pulmonary oedema, concomitant pneumonia, and severe anaemia. Although rare in young children with severe malaria, acute respiratory distress syndrome occurs in 5–25% of adults and up to 29% of pregnant women.[37] Coinfection of HIV with malaria increases mortality.[38] Kidney failure is a feature of blackwater fever, where haemoglobin from lysed red blood cells leaks into the urine.[32]
World Malaria Day 2024: "Accelerating the fight against malaria for a more equitable world",[14]
- World Malaria Day 2023: “Time to deliver zero malaria: invest, innovate, implement”[15]
- World Malaria Day 2022: "Harness innovation to reduce the malaria disease burden and save lives."[16]
- World Malaria Day 2019-2020-2021: "Zero malaria starts with me"[17]
- World Malaria Day 2018: "Ready to beat malaria"
- World Malaria Day 2017: "LETS Close The Gap"
- World Malaria Day 2016: "End Malaria For Good"[18][19][20]
- World Malaria Day 2013-2014-2015: "Invest in the future: defeat malaria"[21]
- World Malaria Day 2012: "Sustain Gains, Save Lives: Invest in Malaria"[22]
- World Malaria Day 2011: "Achieving Progress and Impact"[23]
- World Malaria Day 2009-2010: "Counting malaria out"[24]
- World Malaria Day 2008: "Malaria: a disease without borders"[25]
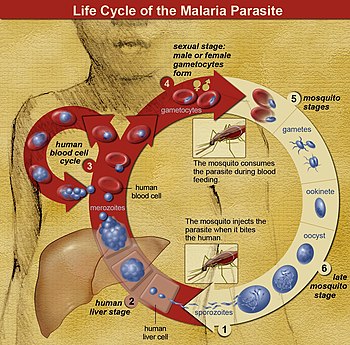
''Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals.[5][6][3] Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches.[1][7] In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death.[1] Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.[3] If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later.[3] In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms.[1] This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria.[1]
Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the Plasmodium group.[3] It is spread exclusively through bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.[3][8] The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood.[3] The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce.[1] Five species of Plasmodium can infect and be spread by humans.[1] Most deaths are caused by P. falciparum, whereas P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae generally cause a milder form of malaria.[1][3] The species P. knowlesi rarely causes disease in humans.[3] Malaria is typically diagnosed by the microscopic examination of blood using blood films, or with antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests.[1] Methods that use the polymerase chain reaction to detect the parasite's DNA have been developed, but they are not widely used in areas where malaria is common, due to their cost and complexity.[9]
The risk of disease can be reduced by preventing mosquito bites through the use of mosquito nets and insect repellents or with mosquito-control measures such as spraying insecticides and draining standing water.[1] Several medications are available to prevent malaria for travellers in areas where the disease is common.[3] Occasional doses of the combination medication sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine are recommended in infants and after the first trimester of pregnancy in areas with high rates of malaria.[3] As of 2020, there is one vaccine which has been shown to reduce the risk of malaria by about 40% in children in Africa.[10][11] A pre-print study of another vaccine has shown 77% vaccine efficacy, but this study has not yet passed peer review.[needs update][12] Efforts to develop more effective vaccines are ongoing.[11] The recommended treatment for malaria is a combination of antimalarial medications that includes artemisinin.[13][14][1][3] The second medication may be either mefloquine, lumefantrine, or sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine.[15] Quinine, along with doxycycline, may be used if artemisinin is not available.[15] It is recommended that in areas where the disease is common, malaria is confirmed if possible before treatment is started due to concerns of increasing drug resistance.[3] Resistance among the parasites has developed to several antimalarial medications; for example, chloroquine-resistant P. falciparum has spread to most malarial areas, and resistance to artemisinin has become a problem in some parts of Southeast Asia.[3]
The disease is widespread in the tropical and subtropical regions that exist in a broad band around the equator.[16][1] This includes much of sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Latin America.[3] In 2020 there were 241 million cases of malaria worldwide resulting in an estimated 627,000 deaths. Approximately 95% of the cases and deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. Rates of disease have decreased from 2010 to 2014 but increased from 2015 to 2020.[4] Malaria is commonly associated with poverty and has a significant negative effect on economic development.[17][18] In Africa, it is estimated to result in losses of US$12 billion a year due to increased healthcare costs, lost ability to work, and adverse effects on tourism
- Hits: 1174
- Video Field: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iKPw6-cTpIA
We're for all- ALL are for us for the greater interest of Humanism-Truth-Facts-Friendship-Unity-Participation including Physico-Mental Sound Health with Spirituality enrichment through ''TOTAL HEALTH SOLUTION'' to a Well-furnished GOALofTruth alloted for all in real sense ;
From wikipedia & other reliable sources ( Poets, Writers, Thinkers, Researchers, Free Lancers, Philosophers, Theologists, Scientists, Orators, Sociologists and Photographers +Artists-Musicians & etc.) we can learn as follows :
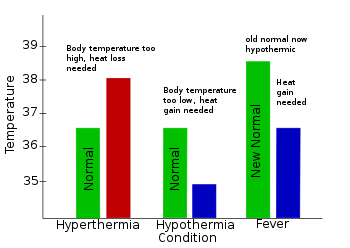
''Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point.[5][6][12][7] There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between 37.2 and 38.3 °C (99.0 and 100.9 °F) in humans.[1][7][8] The increase in set point triggers increased muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills.[2] This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat.[3] When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes flushed, and may begin to sweat.[3] Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children.[4] Fevers do not typically go higher than 41 to 42 °C (106 to 108 °F).[6]
A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening.[13] This includes viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections—such as influenza, the common cold, meningitis, urinary tract infections, appendicitis, Lassa, COVID-19, and malaria.[13][14] Non-infectious causes include vasculitis, deep vein thrombosis, connective tissue disease, side effects of medication or vaccination, and cancer.[13][15] It differs from hyperthermia, in that hyperthermia is an increase in body temperature over the temperature set point, due to either too much heat production or not enough heat loss.[1]
Treatment to reduce fever is generally not required.[2][9] Treatment of associated pain and inflammation, however, may be useful and help a person rest.[9] Medications such as ibuprofen or paracetamol (acetaminophen) may help with this as well as lower temperature.[9][10] Children younger than three months require medical attention, as might people with serious medical problems such as a compromised immune system or people with other symptoms.[16] Hyperthermia requires treatment.[2]
Fever is one of the most common medical signs.[2] It is part of about 30% of healthcare visits by children[2] and occurs in up to 75% of adults who are seriously sick.[11] While fever evolved as a defense mechanism, treating a fever does not appear to improve or worsen outcomes.[17][18][19] Fever is often viewed with greater concern by parents and healthcare professionals than is usually deserved, a phenomenon known as fever phobia.
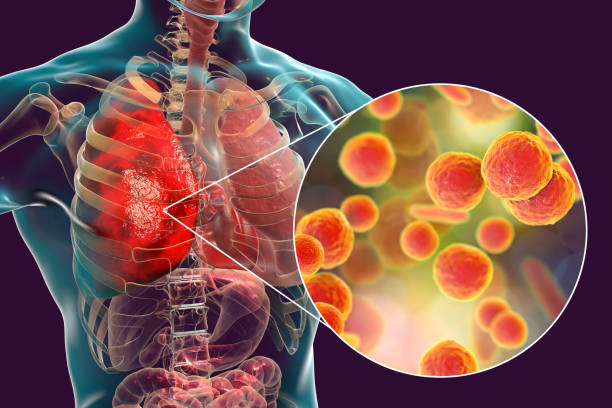
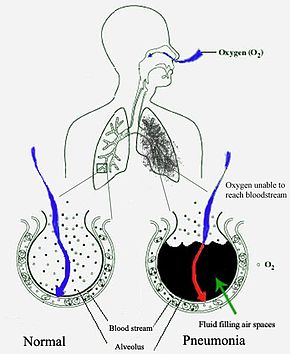
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli.[3][14] Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing.[15] The severity of the condition is variable.[15]
Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms.[a] Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination.[8] Chest X-rays, blood tests, and culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis.[8] The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia.[18]
Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, a poor ability to cough (such as following a stroke), and a weak immune system.[5][7]
Vaccines to prevent certain types of pneumonia (such as those caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria, linked to influenza, or linked to COVID-19) are available.[10] Other methods of prevention include hand washing to prevent infection, not smoking, and social distancing.[10]
Treatment depends on the underlying cause.[19] Pneumonia believed to be due to bacteria is treated with antibiotics.[11] If the pneumonia is severe, the affected person is generally hospitalized.[19] Oxygen therapy may be used if oxygen levels are low.[11]
Each year, pneumonia affects about 450 million people globally (7% of the population) and results in about 4 million deaths.[12][13] With the introduction of antibiotics and vaccines in the 20th century, survival has greatly improved.[12] Nevertheless, pneumonia remains a leading cause of death in developing countries, and also among the very old, the very young, and the chronically ill.[12][20] Pneumonia often shortens the period of suffering among those already close to death and has thus been called "the old man's friend